Introduction
The industrial enzymes sector stands at the intersection of challenges and opportunities, embodying a dynamic landscape shaped by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving consumer demands. Enzymes, biological catalysts that drive biochemical reactions, have become pivotal players in various industries, ranging from food and beverage to textiles, biofuels, and pharmaceuticals.
As we delve into the realm of industrial enzymes, it becomes evident that this sector is not immune to challenges. Regulatory complexities, sustainability concerns, and the need for cost-effective solutions pose significant hurdles. The intricate web of compliance requirements, especially in the wake of a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly practices, challenges companies to innovate while adhering to stringent standards.
What does industrial enzymes mean?
Industrial enzymes refer to specialized proteins that act as catalysts in various industrial processes. These enzymes are derived from microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi or produced through genetic engineering techniques. Unlike traditional chemical catalysts, industrial enzymes operate under mild conditions, offering specificity and efficiency in catalyzing biochemical reactions.
These enzymes find applications across a broad spectrum of industries, playing a crucial role in processes such as manufacturing, food and beverage production, textiles, biofuels, and pharmaceuticals. Their catalytic abilities enable them to accelerate specific chemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
Here are some key points to understand about industrial enzymes:
- Biological Catalysts: Enzymes are biological molecules that facilitate and accelerate chemical reactions. They are typically specific to particular substrates, meaning they work on specific types of molecules.
- Diverse Applications: Industrial enzymes are utilized in various industrial sectors for tasks such as breaking down complex molecules, modifying chemical structures, improving production efficiency, and reducing environmental impact.
- Sustainability: The use of industrial enzymes is often associated with sustainability practices. Enzymes can replace or reduce the need for harsh chemicals in industrial processes, leading to more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient production methods.
- Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering: Advances in biotechnology and genetic engineering have enabled the optimization and customization of enzymes for specific industrial applications, enhancing their efficiency and versatility.
Growth rate in industrial enzymes market
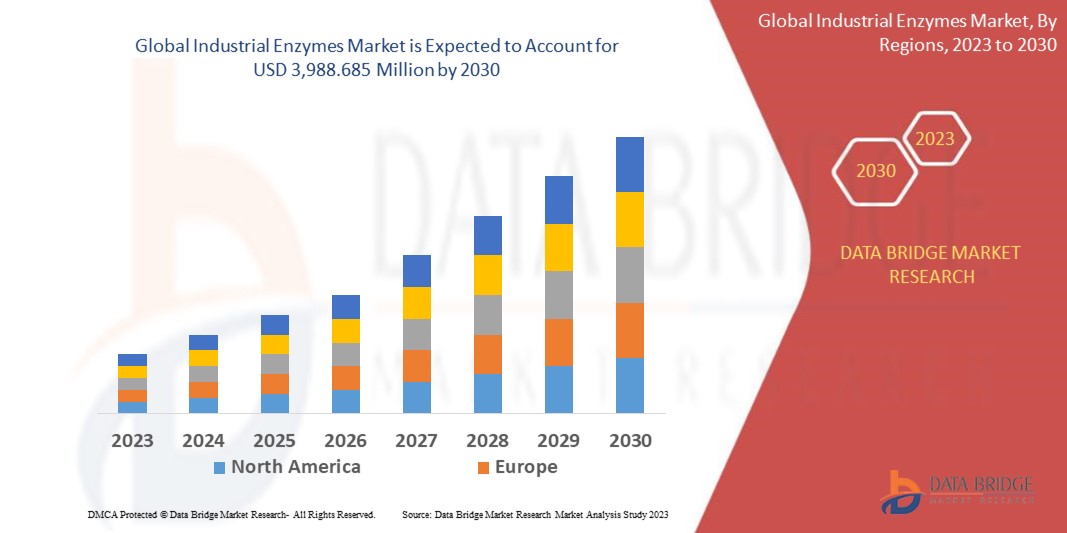
According to the analysis conducted by Data Bridge Market Research, the industrial enzymes market is poised for robust growth, projecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 21.0% throughout the forecast period. This signifies a substantial increase in market value, rising from USD 2,877 million in 2022 to an anticipated USD 3,988.685 million by the year 2030. The comprehensive market reports provided by Data Bridge Market Research not only offer key insights into market scenarios, including market value, growth rate, segmentation, and geographical coverage, but they also encompass a wealth of additional information crucial for stakeholders. These insights include in-depth expert analysis, detailed production and capacity data presented on a company-wise geographical basis, network layouts outlining distributor and partner relationships, and a thorough and updated analysis of price trends. Furthermore, the reports address critical aspects such as deficit analysis within the supply chain and demand dynamics. With this comprehensive approach, Data Bridge Market Research aims to provide a holistic understanding of the industrial enzymes market, empowering businesses and industry players with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Industrial Enzymes Sector
The Industrial Enzymes Sector presents a landscape characterized by a dynamic interplay of challenges and opportunities, shaping the trajectory of innovation and growth within various industries. These biological catalysts have become integral to processes spanning from manufacturing and food production to pharmaceuticals and biofuels. Understanding the challenges and opportunities within this sector is crucial for stakeholders navigating an environment shaped by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and evolving market demands.
Challenges:
- Regulatory Complexity: The industrial enzymes sector faces challenges related to evolving regulatory frameworks. Compliance with stringent standards, particularly in the context of environmental sustainability, demands continuous adaptation and innovation.
- Cost Pressures: The production and application of industrial enzymes can be cost-intensive. Companies encounter challenges in balancing the cost of enzyme production with the economic feasibility of their widespread use across industries.
- Public Perception and Acceptance: Despite their benefits, the acceptance of industrial enzymes can be hindered by public perception. Clear communication and education are essential to dispel misconceptions and build trust among consumers and regulatory bodies.
- Substrate Specificity: Enzymes often exhibit specificity to certain substrates. This can limit their applicability in diverse industrial processes, necessitating the development of a broad range of enzymes for different applications.
Opportunities:
- Sustainability Imperative: The global shift toward sustainable practices provides a significant opportunity for the industrial enzymes sector. Enzymatic processes often align with sustainability goals by reducing the environmental impact of industrial activities.
- Biotechnological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in biotechnology and genetic engineering unlock new possibilities for enzyme optimization. Tailoring enzymes for specific tasks and applications enhances their efficiency, opening avenues for innovation.
- Emerging Markets: Growing economies and emerging markets present untapped opportunities for the industrial enzymes sector. As industries expand in these regions, the demand for efficient and sustainable industrial processes is likely to increase.
- Diversification of Applications: Industrial enzymes find applications across a spectrum of industries. Continued research and development efforts to discover new applications and improve existing ones can drive market growth and diversification.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Collaborations between enzyme manufacturers, research institutions, and industries can foster innovation and accelerate the development of novel enzyme-based solutions. Partnerships facilitate the pooling of resources and expertise.
For more information about challenges in industrial enzymes market visit
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-industrial-enzymes-market